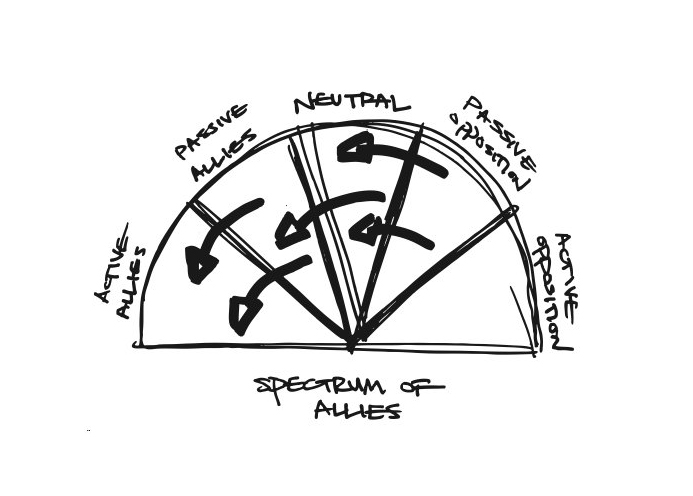
Successful movement-building hinges on being able to see a society in terms of specific blocs or networks, some of which are institutions (unions, churches, schools), others of which are less visible or cohesive, like youth subcultures or demographic groupings. Determine the social blocs at play on a given issue, and work to shift them closer to your position.
An Example
In 1964, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), a major driver of the civil rights movement in the U.S. South, conducted a “spectrum-of-allies style” analysis. They determined that they had a lot of passive allies who were students in the North: these students were sympathetic, but had no entry point into the movement.
To shift these allies from “passive” to “active,” SNCC sent buses north to bring folks down to participate in the struggle under the banner “Freedom Summer.” Students came in droves, and many were deeply radicalized in the process.
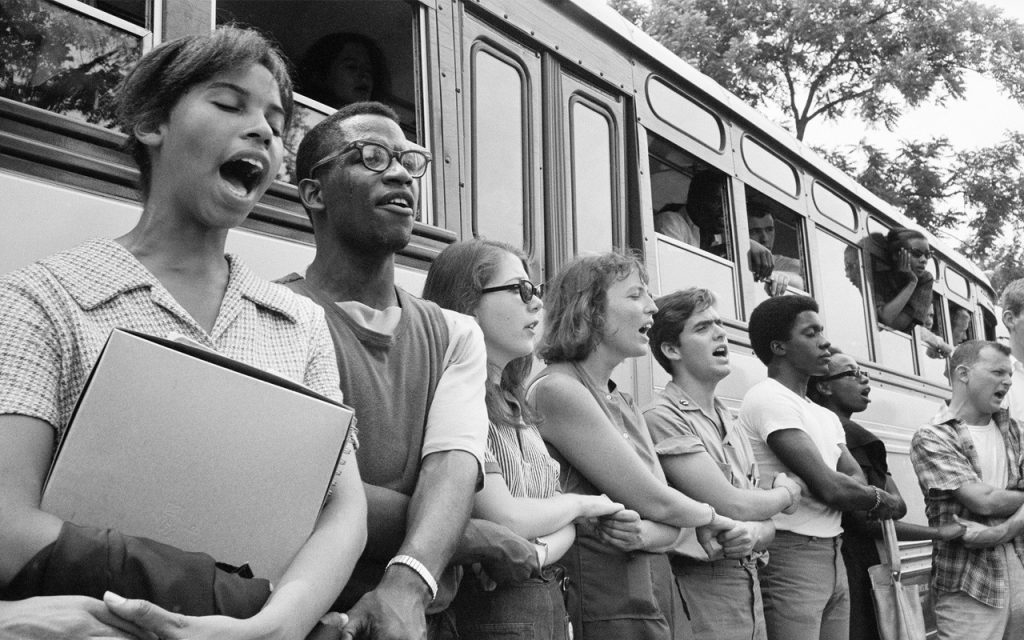

Many wrote letters home to their parents, who suddenly had a personal connection to the struggle. This triggered another shift: their families became passive allies, often bringing their workplaces and social networks with them. The students, meanwhile, went back to school in the fall and proceeded to organize their campuses. More shifts. The result: a profound transformation of the political landscape of the U.S.
